The Power of Plants: A Comprehensive Guide to Plant-Based Nutrition for Weight Loss
Embarking on a weight loss journey can feel overwhelming, with countless diets and strategies promising quick results. However, sustainable and healthy weight management often lies in embracing a whole-foods, plant-based approach. This article delves deep into the science and practicalities of using plant-based nutrition as a powerful tool for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Understanding Plant-Based Nutrition
A plant-based diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods derived from plants. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes (beans, lentils, peas), nuts, and seeds. While there are variations, a focus on these nutrient-dense foods forms the cornerstone of this dietary approach.
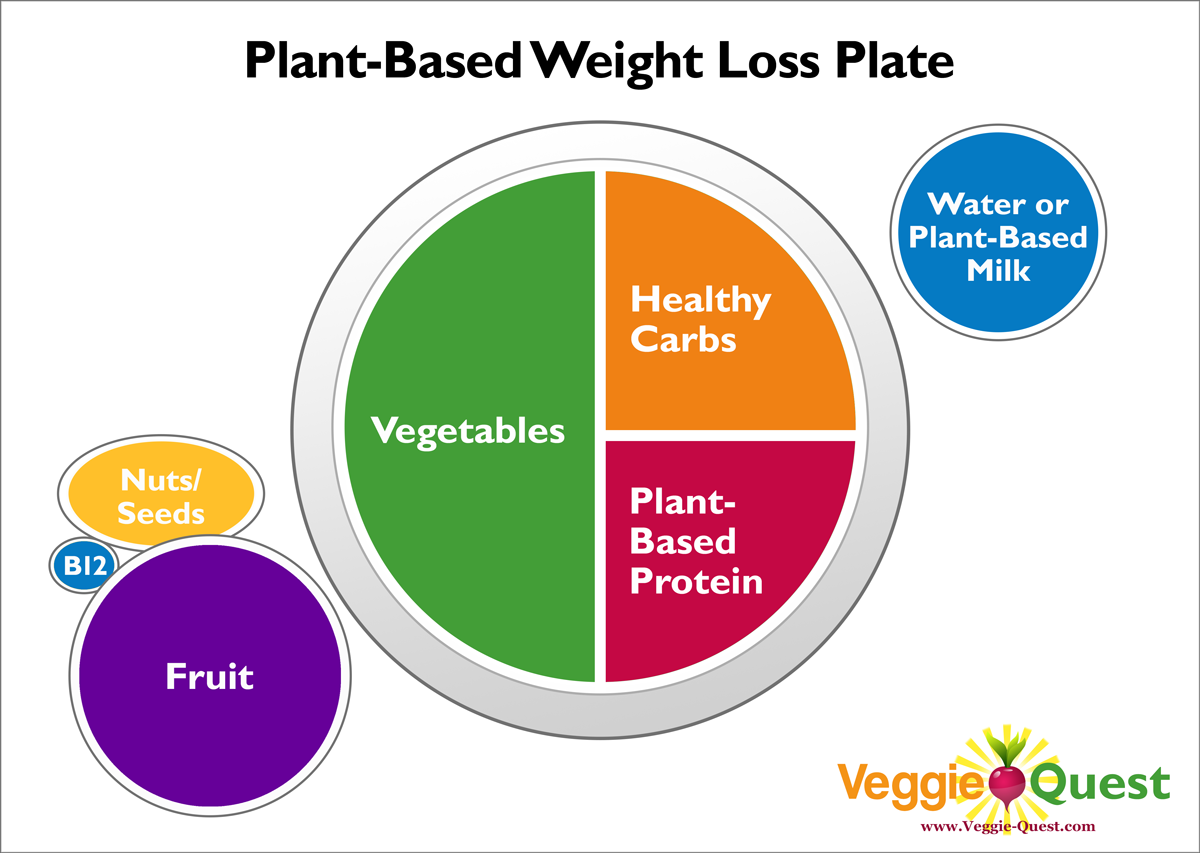
Why Plant-Based Diets Support Weight Loss
Several key characteristics of plant-based diets contribute to their effectiveness in promoting weight loss:
High in Fiber
Plant-based foods are naturally rich in dietary fiber. Fiber adds bulk to meals without adding significant calories, promoting feelings of fullness and satiety. This can help reduce overall calorie intake by preventing overeating. Soluble fiber, found in oats, barley, apples, and legumes, also slows down digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for managing hunger and preventing energy crashes that often lead to unhealthy snacking.

Low in Caloric Density
Many plant-based foods, particularly fruits and vegetables, have a high water content and are naturally low in calories relative to their volume. This means you can eat a larger quantity of food while consuming fewer calories compared to calorie-dense animal products and processed foods. This allows for satisfying meals without hindering weight loss efforts.
Rich in Nutrients
Whole plant foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients support overall health and well-being during weight loss, ensuring the body receives the necessary fuel and protection while reducing calorie intake. This contrasts with many processed “diet” foods that may be low in calories but also lack vital nutrients.
Naturally Lower in Fat (Especially Saturated Fat)
While some plant-based foods like avocados, nuts, and seeds contain healthy fats, a predominantly plant-based diet tends to be lower in overall fat, especially saturated fat found primarily in animal products. Reducing saturated fat intake is beneficial not only for weight management but also for cardiovascular health.
Positive Impact on Gut Microbiota
The high fiber content of plant-based diets promotes a healthy and diverse gut microbiome. Beneficial gut bacteria ferment fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that have been linked to increased satiety hormones, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation – all factors that can positively influence weight management.
Key Plant-Based Food Groups for Weight Loss
Incorporating a variety of foods from the following plant-based groups is crucial for a balanced and effective weight loss plan:
Vegetables: The Cornerstone
Non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce), broccoli, cauliflower, peppers, and zucchini are incredibly low in calories and packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They should form the bulk of your meals, providing volume and nutrients without contributing significantly to calorie intake.
Fruits: Natural Sweetness and Fiber
Fruits offer natural sweetness and are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. Opt for whole fruits over juices to maximize fiber intake. Berries, apples, pears, and citrus fruits are particularly beneficial choices. Be mindful of portion sizes due to their natural sugar content.
Whole Grains: Sustained Energy
Whole grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat bread provide complex carbohydrates and fiber, leading to a slow and steady release of energy. This helps prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes, reducing cravings and promoting satiety. Choose whole, unprocessed grains over refined grains (white bread, pasta) which are lower in fiber and nutrients.
Legumes: Protein and Fiber Powerhouse
Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are excellent sources of plant-based protein and fiber. They are incredibly satiating and can help build and maintain lean muscle mass, which is important for a healthy metabolism during weight loss. Incorporate them into soups, stews, salads, and as meat alternatives.
Nuts and Seeds: Healthy Fats in Moderation
Nuts and seeds are rich in healthy unsaturated fats, protein, and fiber. While beneficial, they are also calorie-dense, so moderation is key. Include small portions of almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, and pumpkin seeds in your diet for their nutritional benefits and satiety-promoting properties.
Practical Strategies for Plant-Based Weight Loss
Successfully using plant-based nutrition for weight loss involves more than just eating plants. Here are some practical strategies to implement:
Focus on Whole, Unprocessed Foods
Prioritize whole, minimally processed plant foods over refined and processed options. This means choosing whole grains over white flour products, fresh fruits and vegetables over canned or processed versions, and making your own meals from scratch whenever possible. Processed plant-based foods can be high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and added sugars, hindering weight loss efforts.
Build Balanced Meals
Ensure each meal includes a good source of fiber (vegetables, whole grains, legumes), protein (legumes, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds), and healthy fats (avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil in moderation). This combination promotes satiety and provides sustained energy.
Be Mindful of Portion Sizes
Even healthy plant-based foods contain calories. Pay attention to portion sizes, especially for calorie-dense foods like nuts, seeds, avocados, and dried fruits. Using smaller plates and being mindful of your hunger and fullness cues can be helpful.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is crucial for overall health and can also aid in weight loss by promoting feelings of fullness and supporting metabolic processes. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, so staying hydrated can prevent unnecessary snacking.
Limit Added Sugars and Unhealthy Fats
Be mindful of hidden added sugars in processed foods, sauces, and drinks. Similarly, limit the use of excessive amounts of oils and unhealthy fats in cooking. Opt for healthier cooking methods like steaming, baking, or grilling.
Plan Your Meals and Snacks
Planning your meals and snacks in advance can help you make healthier choices and avoid impulsive, less nutritious options when hunger strikes. Keep healthy plant-based snacks like fruits, vegetables with hummus, or a small handful of nuts readily available.
Learn to Read Food Labels
Pay attention to nutrition information and ingredient lists on packaged foods. Be aware of serving sizes, calorie content, fiber content, and the presence of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive sodium.
Be Patient and Consistent
Sustainable weight loss is a gradual process. Focus on making consistent healthy choices rather than seeking quick fixes. Celebrate small victories and be patient with yourself as you adopt a plant-based lifestyle.
Addressing Potential Concerns
While plant-based diets offer numerous benefits for weight loss and overall health, some individuals may have concerns about nutrient adequacy. Here’s how to address them:
Protein: Abundant in Plants
Many plant foods are excellent sources of protein, including legumes, tofu, tempeh, edamame, quinoa, nuts, seeds, and even some vegetables and whole grains. By consuming a varied plant-based diet, it’s entirely possible to meet your protein needs.
Vitamin B12: Consider Supplementation
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products. Individuals following a strict plant-based diet should consider supplementing with vitamin B12 or consuming fortified foods like nutritional yeast or plant-based milks.
Iron: Enhance Absorption
Plant-based sources of iron (non-heme iron) are not as readily absorbed as heme iron found in animal products. Enhance iron absorption by consuming iron-rich plant foods alongside vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Choose Plant-Based Sources
Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids like flax seeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements in your diet to ensure adequate intake of these essential fats.
Calcium and Vitamin D: Plenty of Plant-Based Options
Calcium can be found in leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milks, tofu, and sesame seeds. Vitamin D can be obtained through sunlight exposure and fortified foods. Supplementation may be necessary, especially during winter months or for individuals with limited sun exposure.
Conclusion: Embracing Plants for Sustainable Weight Loss
A well-planned, whole-foods plant-based diet offers a powerful and sustainable approach to weight loss. By emphasizing fiber-rich, nutrient-dense, and calorie-conscious plant foods, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight while enjoying numerous other health benefits. While it requires mindful planning and attention to potential nutrient considerations, the long-term rewards of a plant-based lifestyle extend far beyond weight management, promoting overall well-being and a healthier relationship with food. Embracing the power of plants can be a transformative step towards a healthier and happier you.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/EW-Meal-Plans-Healthy-Weight-Gain-Day-4-1x1-alt-81577102cff74485ac146541976d8b22.jpg?resize=200,135&ssl=1)

